In today’s quickly changing world, technology is transforming industry operations. The change from automation to data-driven decision-making is so profound that it has its own name: Industry 4.0. But what exactly does Industry 4.0 meaning, and why should firms and individuals worry about it? This guide explains everything down in a straightforward and relatable manner.
What is this in Simple Words?
At its core, the term Industry 4.0 refers to the fourth industrial revolution—a period in which advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, cloud computing, and big data work together to make manufacturing smarter and more efficient.
Imagine factories and systems that can “talk” to one another, analyze data in real time, and change processes without the need for human interaction. This eliminates errors, improves performance, and saves firms money.
The idea is straightforward: to make factories, supply chains, and enterprises smarter, faster, and more connected. Consider machines that can communicate with one another, forecast when they require repairs, and automatically change production schedules—all without waiting for human intervention. This is the actual essence of Industry 4.0.
The Evolution Behind Industry 4.0
Also Read
To better comprehend the meaning of Industry 4.0, it is helpful to look back in history:
Industry 1.0: The Power of Steam
In the late 18th century, manufacturers began to use water and steam power. This marked the beginning of mechanization and the end of handcrafted mass goods.
Industry 2.0: Electricity and Mass Production.
Electricity revolutionized the nineteenth century. Assembly lines enabled large-scale manufacturing, lowering costs and improving speed.
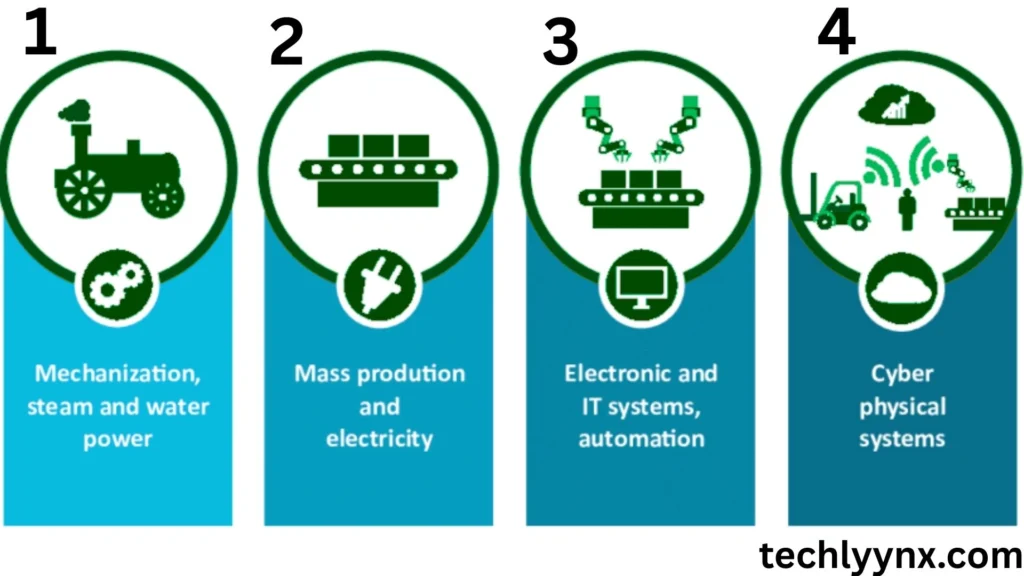
Industry 3.0: Electronics and Automation.
Beginning in the twentieth century, computers and electronics elevated productivity to new heights. Automation systems minimized human error and improved precision.
Industry 4.0: Smart and Connected Systems.
Today, Industry 4.0 signifies the era of networked machines and data-driven decisions, in which technology not only supports humans but also learns and adapts.
Key Features of Industry 4.0
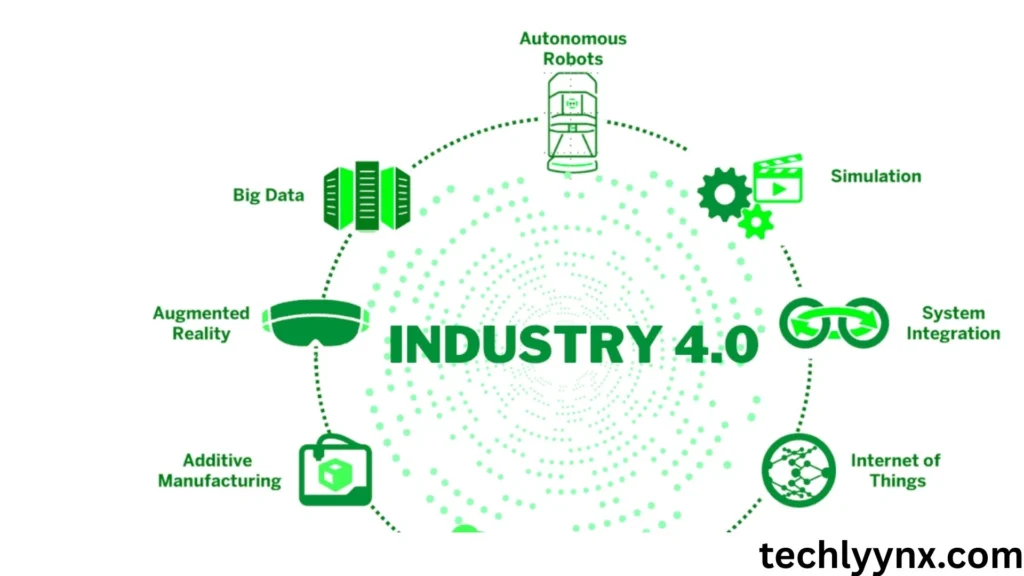
The features that best define Industry 4.0 are:
- Connectivity refers to the smooth communication between machines, devices, and sensors.
- Data Utilization: Real-time analytics can assist optimize production.
- Automation refers to processes that require minimal human interaction.
- Customization: Products can be swiftly adjusted to meet the specific needs of customers.
- Smart Decision Making: Artificial intelligence and machine learning enable systems to adapt and improve.
The Role of Technologies in Industry 4.0
Let’s look at the technologies that define the Industry 4.0 meaning:
- Internet of Things (IoT): Devices and sensors embedded in machines allow them to share information seamlessly.
- Big Data and Analytics: Data collected from operations helps companies predict outcomes and optimize production.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Enables predictive maintenance, smarter supply chains, and intelligent decision-making.
- Robotics: Modern robots are flexible, precise, and capable of working safely alongside humans.
- Cloud Computing: Stores massive amounts of data and provides access from anywhere.
- Cybersecurity: Protects digital systems from cyber threats, which are more important than ever in connected industries.
Benefits
Understanding Industry 4.0’s meaning also entails appreciating its benefits:
Increased Efficiency – Interconnected machines minimize downtime and improve production efficiency.
- Cost Savings – Effective resource management reduces waste and overall costs.
- Improved Quality: Smart monitoring lowers errors, resulting in improved product standards.
- Flexible Production – Factories can easily transition from one product to another dependent on demand.
- Sustainability – Smarter processes consume less energy and generate less waste, contributing to environmental goals.
Challenges Connected with Industry 4.0
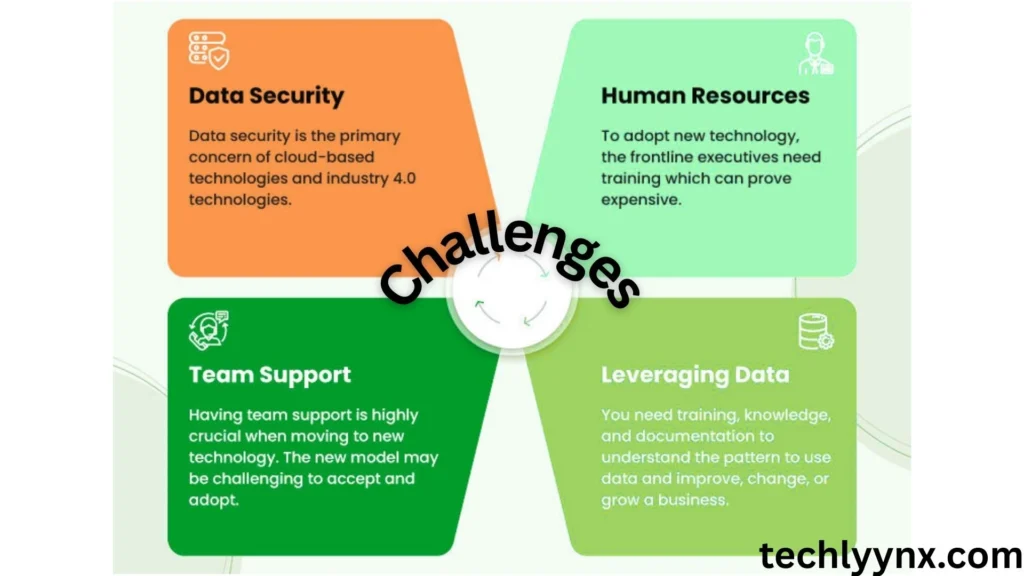
While the benefits are obvious, the Industry 4.0 definition also includes certain challenges:
High initial costs: Upgrading factories and systems demands a significant investment.
Cybersecurity Risks: As systems become more networked, there are greater chances for cyberattacks.
Employees require new abilities to operate with innovative machinery and technologies.
Resistance to Change: Some businesses and employees are hesitant to adopt new systems.
In Everyday Life
Even if you do not work in manufacturing, the concept of Industry 4.0 has an impact on your daily life. For example:
- Smart refrigerators that monitor food expiration dates.
- Ride-sharing applications that use artificial intelligence to improve routes.
- Healthcare equipment that monitor heart rates and offer notifications.
- Online shopping platforms that anticipate what you’ll want to purchase next.
Industry 4.0 is more than simply factories; it is about building a smarter, more connected world.
The Future of Work in Industry 4.0
The impact on jobs is an important aspect of Industry 4.0. While automation may replace some jobs, it also opens up new opportunities. Workers with expertise in AI, robots, and data analytics will be in high demand. Collaboration between people and machines will be the norm.
Instead of dreading automation, employees may prepare by honing their digital abilities and learning how to collaborate with modern technology.
Why Businesses Must Care About
Adopting Industry 4.0 is no longer an option for organizations; it is a need. Companies that embrace smart manufacturing may increase productivity, lower costs, and offer higher-quality products. Those who oppose risk getting left behind.
Small and medium-sized businesses, as well as major corporations, can reap benefits. Cloud solutions and low-cost smart tools are making Industry 4.0 available to everyone.
Final Thoughts
To summarize, Industry 4.0 is much more than simply technology; it is a revolution that is transforming the way industries run, things are manufactured, and people live. Industry 4.0 is transforming the future by merging AI, robotics, IoT, and data analytics to create more efficient, sustainable, and customer-centric systems.
Understanding Industry 4.0 is critical for anyone who owns a business, is a student, or simply wants to know what the future holds. It’s not just the future of manufacturing; it’s the future of the entire world.

